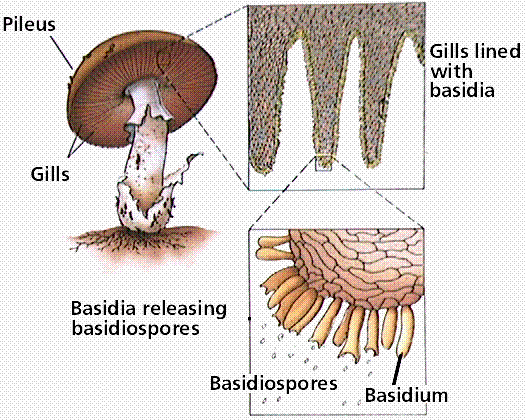
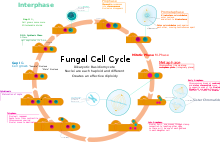
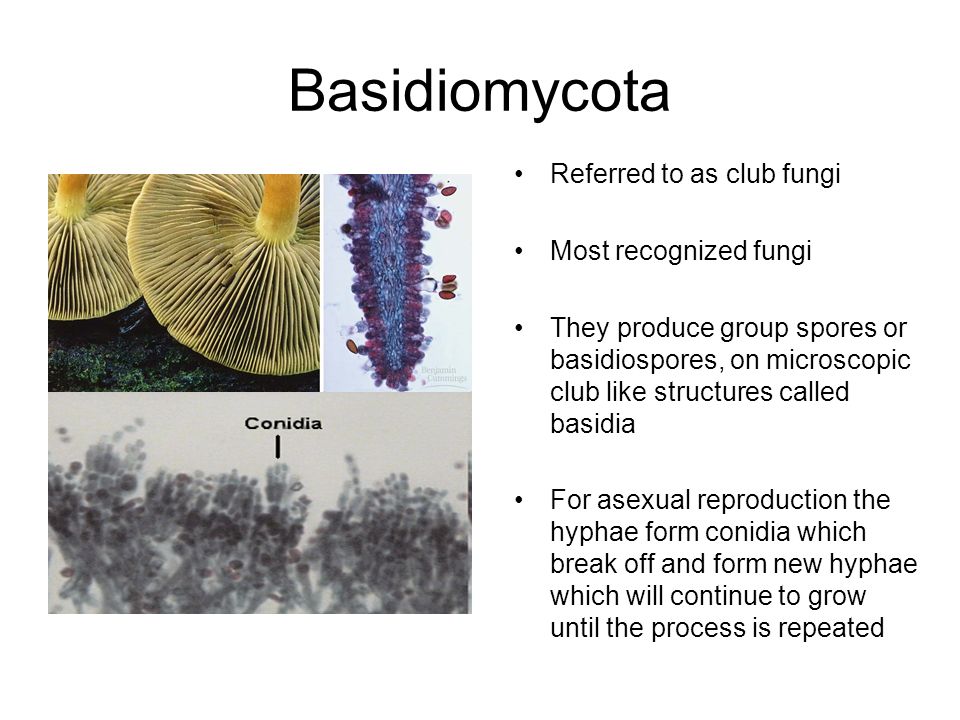
Two Major Groups Classifying fungi into ascomycetes and basidiomycetes The (macro) fungi that are dealt with in this website can be divided into two broad groups, called ascomycetes and basidiomycetes, depending on how their sexual spores are formedAll the macrofungi produce sexual spores, which result from the combination of genetic information from two parentsA fungus ( plural fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, those being Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and ChromistaObserve a prepared slide of the mushroom Coprinus under the compound microscope A Focus using the 4X lens and locate the edge of a gill Observe with the 10X and 40X lenses B Observe the clubshaped structures (called basidia) on which spores are produced The club fungi derive their name from these clubshaped structures

Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual
Club fungi under microscope
Club fungi under microscope-The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, 33 Zygosporeforming Fungi These organisms were formerly classified in a group called the Zygomycota because they sexually reproduce by forming a structure called a zygospore However, they have since been broken into several different lineages




Lab Practical 1 Survey Of The Kingdom Fungi Flashcards Quizlet
Start studying Club Fungi, Lichens, and Mycorrhizae Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsBacteria species E coli and S aureus under the microscope with different magnifications Bacteria are among the smallest, simplest and most ancient livingAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators
Basidiomycota The Club Fungi The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hyphaFungal hyphae are stained with lactophenol cotton blue solution and observed under microscope and images captured (Olympus BX51 compound microscope attached with Olympus DP71 digital camera) Basidiospore samples can be prepared for scanning electron microscopy using the method described by De Melo and Faull 51 to reveal the spore size and morphologyHow to observe yeast under the microscope Yeast cells are some of the smallest eukaryotic organisms with a diameter of only 5 to 10 micrometers per cell, and thus need to be viewed under high magnification optical microscopes, set to a high
Mushrooms, also known as fungi or toadstools, are the sporebearing fruiting body of a fungus The mushroom typically grows above ground or on top of its food source (on a log, or out the side of a mossy tree) A mushroom has a stem and a cap along with gills The gills of the mushroom are often examined under a microscope to identify theThe Basidiomycota (basidiomycetes) are fungi that have basidia (clubshaped structures) that produce basidiospores (spores produced through budding) within fruiting bodies called basidiocarps (Figure 8) They are important as decomposers and as food This group includes rusts, stinkhorns, puffballs, and mushrooms Fungal spores are haploid cells that are produced by meiosis and are used to disperse the fungus When they land in a suitable location they germinate and grow Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae The image below was taken by Dr Tammy Oliver using a Leica microscope with a digital camera attached




The Fungi Kingdom Mycology The Study Of Fungi




Biology 141 Qi Chytrid Fungus Zygote Fungi Sac Fungi Club Fungi Flashcards Quizlet
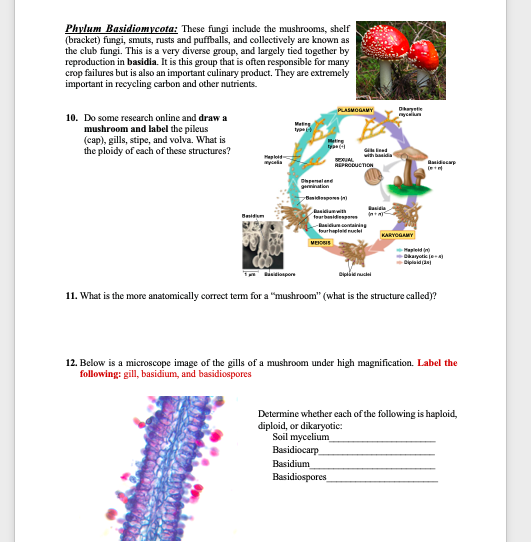
Kingdom Fungi Types, Examples, Morphology, Structure and Importance Fungi belong to their own kingdom Compared to higher plants and animals, they obtain their nutrition through a range of ways including degradation of organic material and symbiosis (as lichen) among others As such, they are categorized as heterotrophic because they are unable to synthesize their own foodUnder the microscope, it should now be possible to see any of the important characteristics which will be used for identification These include the spores, acsi (sacs containing the spores), paraphyses (infertile structures between the asci), hairs, andThe fungi comprise a diverse group of organisms that are heterotrophic and typically saprozoic In addition to the wellknown macroscopic fungi (such as mushrooms and molds), many unicellular yeasts and spores of macroscopic fungi are microscopic For this reason, fungi are included within the field of microbiology




Fungi Microbiology




Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Coprinus Puccinia Graminis Microscope Slides Carolina Com
In the 1900s the microscopic features became more important so, while all of the features mentioned below are still very useful for identification, their role in classification is often much reduced Of prime importance is the type of fruiting body (eg mushroom, puffball, cup fungus, polypore, etc (SEE TYPES OF FUNGI SECTION) Basidiomycota The Club Fungi The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hyphaObserve preserved Peziza (cup fungus) using a dissecting microscope Observe a slide of Peziza at scanning, low, and high power magnification Find an ascus and




Fungi Organismal Biology



Microscopic Volatile Spores Of Puffball Fungus Lycoperdon Basidiomycota Is A Genus Of Puffball Mushrooms Stock Image Image Of Fungi Particles
Basidiomycota The Club Fungi The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hyphaFungal hyphae, fruiting bodies and, in some instances, masses of spores A dissecting microscope is very useful to pinpoint foliage or fungal structures that can be transferred to a glass slide for examination with a compound microscope A dissecting microscope may also be used to scan plant material for mites and small insectsBasidiomycota The Club Fungi The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hyphaThe basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields after



Club Fungi
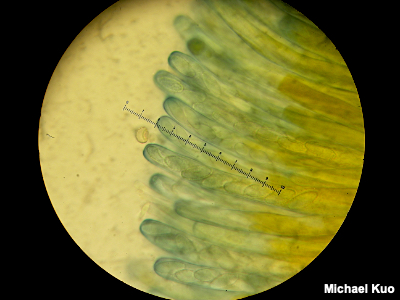



Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms Mushroomexpert Com
Bacteria Under the Microscope Bacteria are singlecelled organisms that are defined as prokaryotes, these are organisms that have cells with no defined nucleus or other specialized organelles In total, there are estimated to be millions of species of bacteria, which are diverse in shape, size and many other defining featuresUse the space below to draw a picture of the Penicillium specimen as you viewed it under the microscope Basidiomycota (club fungi) View the mushroom specimens available in the lab Although individual hyphae must be observed under a microscope, the mycelium of a fungus can be very large, with some species truly being "the fungus humongous" The giant Armillaria solidipes (honey mushroom) is considered the largest organism on Earth, spreading across more than 2,000 acres of underground soil in eastern Oregon;




Classification Of Fungi




Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Instruments Direct
It is estimated to be atMUST WATCHPLEASE SUBSCRIBEHere a mushroom is observed under a microscope It's fungal cells and walls are also observedMany of the techniques required are not that difficult to learn, and a decent used microscope can often be picked up for under $400 The best part is, if you are obsessed with mushrooms and live in an area where they do not come up yearround, you can spend quality time with your little friends in the off season
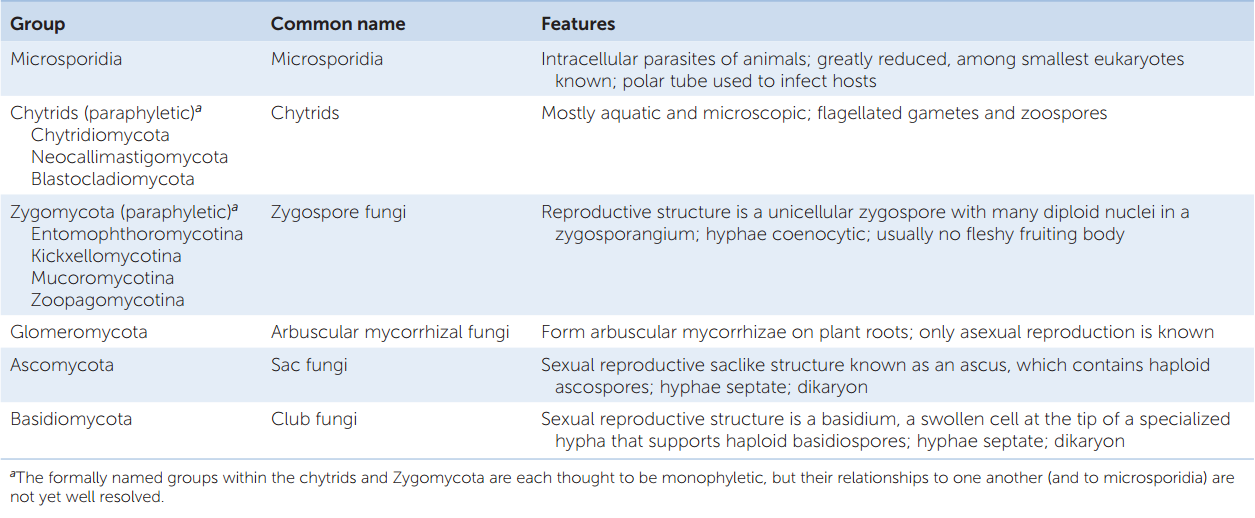



Hillis2e Ch22



3
New hyphae are typically formed by emergence of new tips along existing hyphae by a process called branching, or occasionally growing hyphal tips fork, giving rise to two parallelFungi begin their life as a spore released by adult cells, and they go on to release spores later as well Produced by fruiting bodies such as the edible portion of a mushroom, these spores germinate and grow into new, adult fungi under suitable conditions in terms of temperature, moisture, and availability of organic matter ie, foodThe clavarioid fungi are a group of fungi in the Basidiomycota typically having erect, simple or branched basidiocarps (fruit bodies) that are formed on the ground, on decaying vegetation, or on dead wood They are colloquially called club fungi and coral fungi Originally such fungi were referred to the genus Clavaria ("clavarioid" means Clavarialike), but it is now known that




Club Fungi Microscopic Photography Fungi Abstract
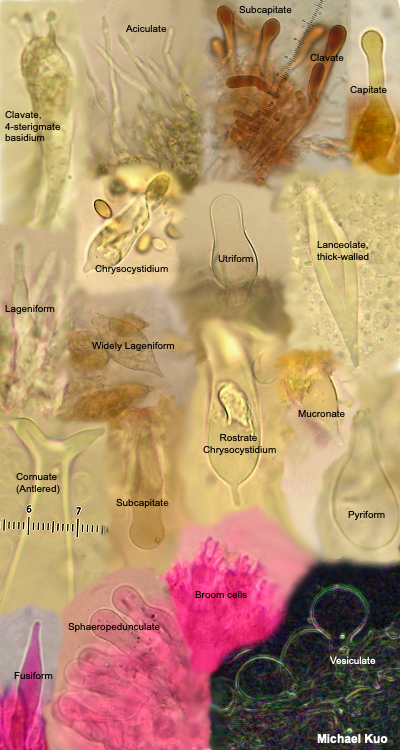



Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms Mushroomexpert Com
The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell ofMicroscopic fungi are eukaryotic, heterotrophic microorganisms that fail to show any cellular differentiation into true tissues like root, stem or leaf and in which vascular system is absent B Characteristics of Fungi The major distinguishing characteristics of fungi are given belowMold fungus on rotten tomato under the microscope fungi microscope stock pictures, royaltyfree photos & images yeast cells, sem fungi microscope stock illustrations Penicillium chrysogenum, mold that produces penicillin, seen on scanning electron microscopy




Scanning Electron Microscope Blog April 13




Club Fungus Home Facebook
The Basidiomycota (basidiomycetes) are fungi that have basidia (clubshaped structures) that produce basidiospores (spores produced through budding) within fruiting bodies called basidiocarps ( Figure 532 ) They are important as decomposers and as food This group includes rusts, stinkhorns, puffballs, and mushroomsMicroscopes and the Amateur Mycologist a Beginner's Guide The information below is a summarized extract from Pat O'Reilly's latest book, 'Fascinated by Fungi'For full details and sample pages see our Bookshop, where you can order an authorsigned copy online (The book also contains a glossary of mycological terms, and we have a summarised version here to helpThe fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha This group also includes shelf fungus, which cling to the bark of trees like small shelves




Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual




Basidia Under Microscope Youtube
Exercise 3) Spore observation under a microscope Using your forceps, tear of a small piece of lamellae (gill) from the fungi and mount in water Do this again in Meltzer's ReagentAdd cover slipGently squish the tissue under the cover slip with an eraserFollow these steps when mounting slides onto the microscopeMold under the Microscope The Fungi Kingdom Molds While there are many types of Fungi, MicroscopeMaster will focus on mold under the microscope here Fungi is a taxonomic Kingdom that is composed of well over 99,000 species including yeast, molds, smuts andFungi vary widely in size and shape, from unicellular, microscopic organisms to multicellular forms easily seen with the naked eye Individual cells range from 1 µ to 30 µ Microscopic fungi exist as either molds or yeasts or both Internally, fungal cells are fairly typical eucaryotic cells (b) Molds
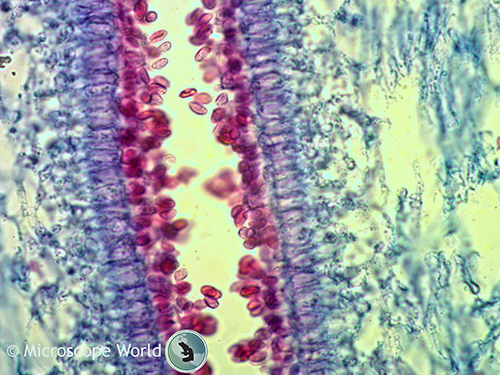



Mushrooms Under The Microscope
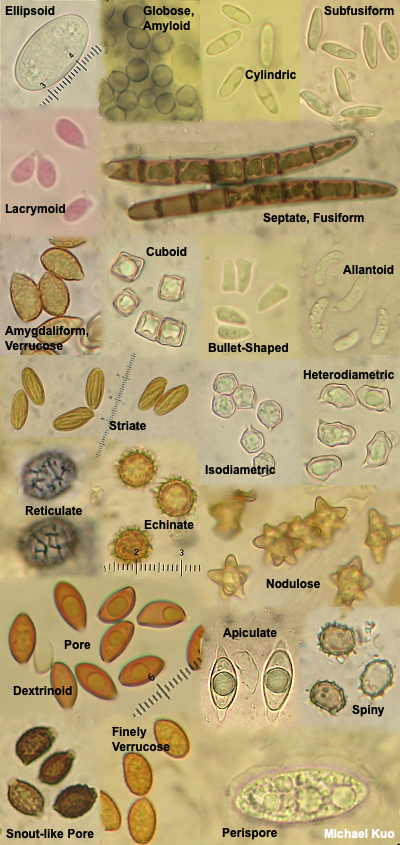



Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms Mushroomexpert Com
27 Yeast under microscope Yeasts are unicellular eukaryotic organisms that are mostly found in plants and soil Some yeasts are also found on the surface of the skin and even inside the body of some animals Yeasts mostly exist in41 Microscopic Morphology Most fungi grow as hyphae, which are cylindrical, threadlike structures 2–10 µm in diameter and up to several centimeters in length Hyphae grow at their tips (apices); Basidiomycota The Club Fungi The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha



Fungi
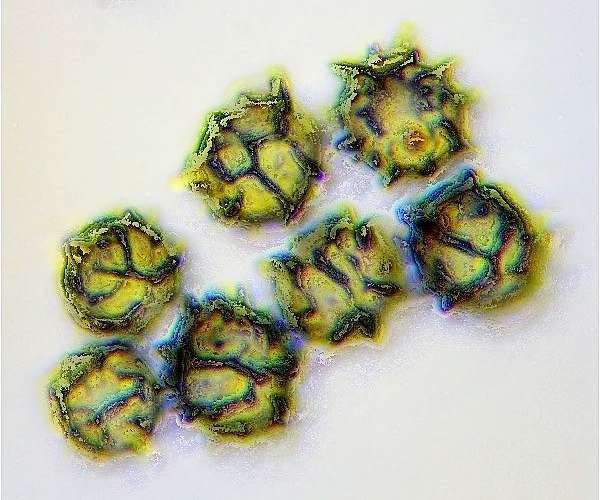



Microscopy Of Spores Hyphae Cystidia Trama To Identify Fungi
Furthermore, what do club fungi look like?Use the lowest magnification on a compound microscope and move the stage so that the entire fungus passes through the field of view You will needDifferent types of fungi under the microscopeActinomyces Aspergillus Candida Albicans Mycellium Penicillium Saccharomyces




The Many Kinds Of Fungi
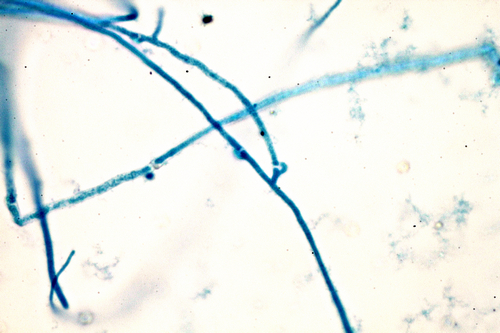



Club Fungi
Most fungi cannot with certainty be identified with the naked eye, and need to be examined under the microscope You will need a microscope providing magnifications from 10 to 1000, a graticule (scale) in one eyepiece, some stains, pipettes, a razor blade or a sharp knife, some tweezers, microscope slides, cover slips and immersion oil (for the high powered microscope objectives)Club Fungi Club fungi (Phylum Basidiomycota) are considered the most highly evolved fungi They are an important group with about 16,000 known species The phylum contains several subgroups whose relationships are not entirely clear One subgroup, the "higher" club fungi, includes those that produce large fruiting bodies such as mushrooms Fungi, the microorganisms that grow on everything from plants to people, can be quite eyecatching when viewed under a microscope
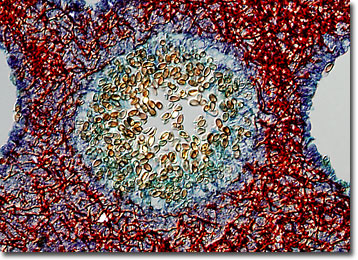



Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Specialized Microscopy Techniques Differential Interference Contrast Image Gallery Mushroom Polyporus Fungus



Phylum Basidiomycota The Basidiomycetes Club Fungi
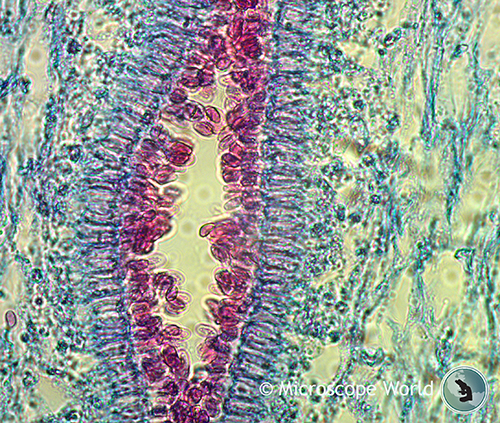



Mushrooms Under The Microscope



Experiment 24 General Medical Microbiology Lab
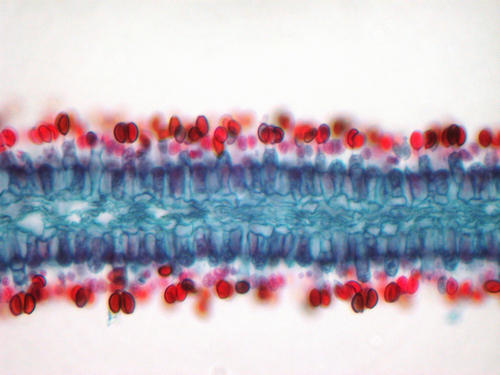



Club Fungi



Teaching The Fungal Tree Of Life Home




Club Fungi Large Images
.jpg)



Superficial Mycoses




Morphology And Ultrastructure Of Fungi Biology Ease




Chapter 24 Fungi Insert Photo Here Representing Chapter




Bio 102 Chapter 23 Fungi Flashcards Quizlet




Fungi Laboratory Notes For Bio 1003




Fungus Wikipedia



Classifications Of Fungi Pdf Free Download




Hillis2e Ch22
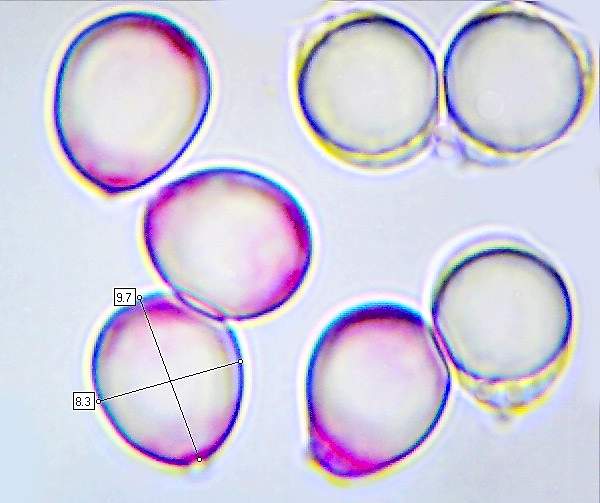



Clavulina Rugosa Wrinkled Club Fungus




Basidiomycota Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Biology 11th Chapter 8 Fungi Youtube




Club Fungi Microscopic Photography Fungi Biology
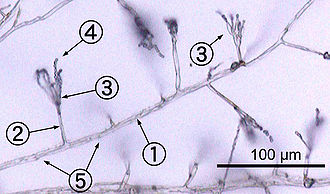



Fungus Wikipedia




Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Instruments Direct
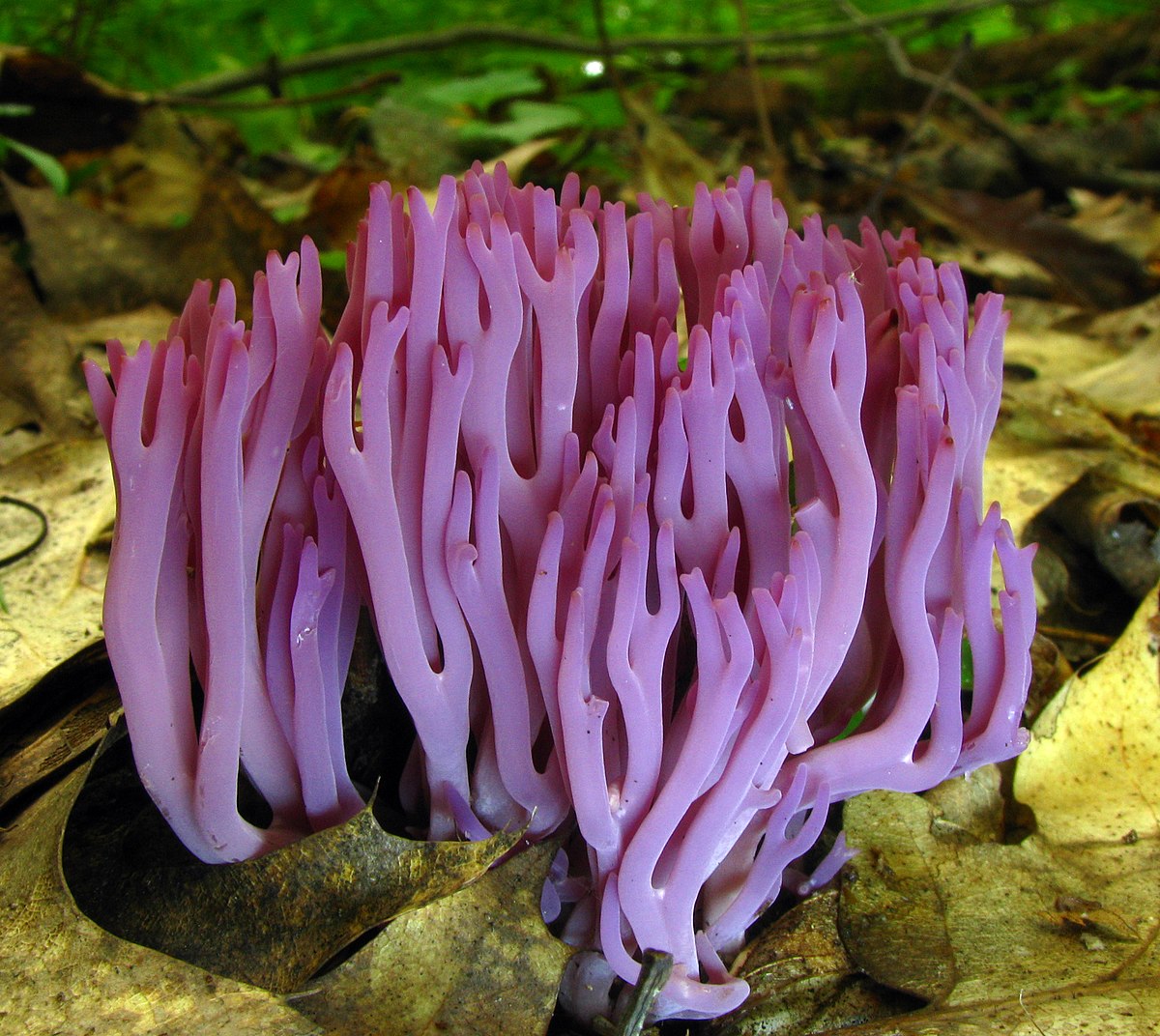




Club Fungus Wiktionary
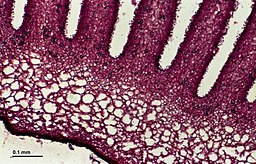



Kingdom Fungi Types Examples Morphology Structure And Importance




Fungi Microbiology



3




The Club Fungi Powerpoint




Fungi Concepts Of Biology




Ascomycota Sac Fungi Basidiomycota Club Fungi Victoria Willis Quyen Mac Ppt Download
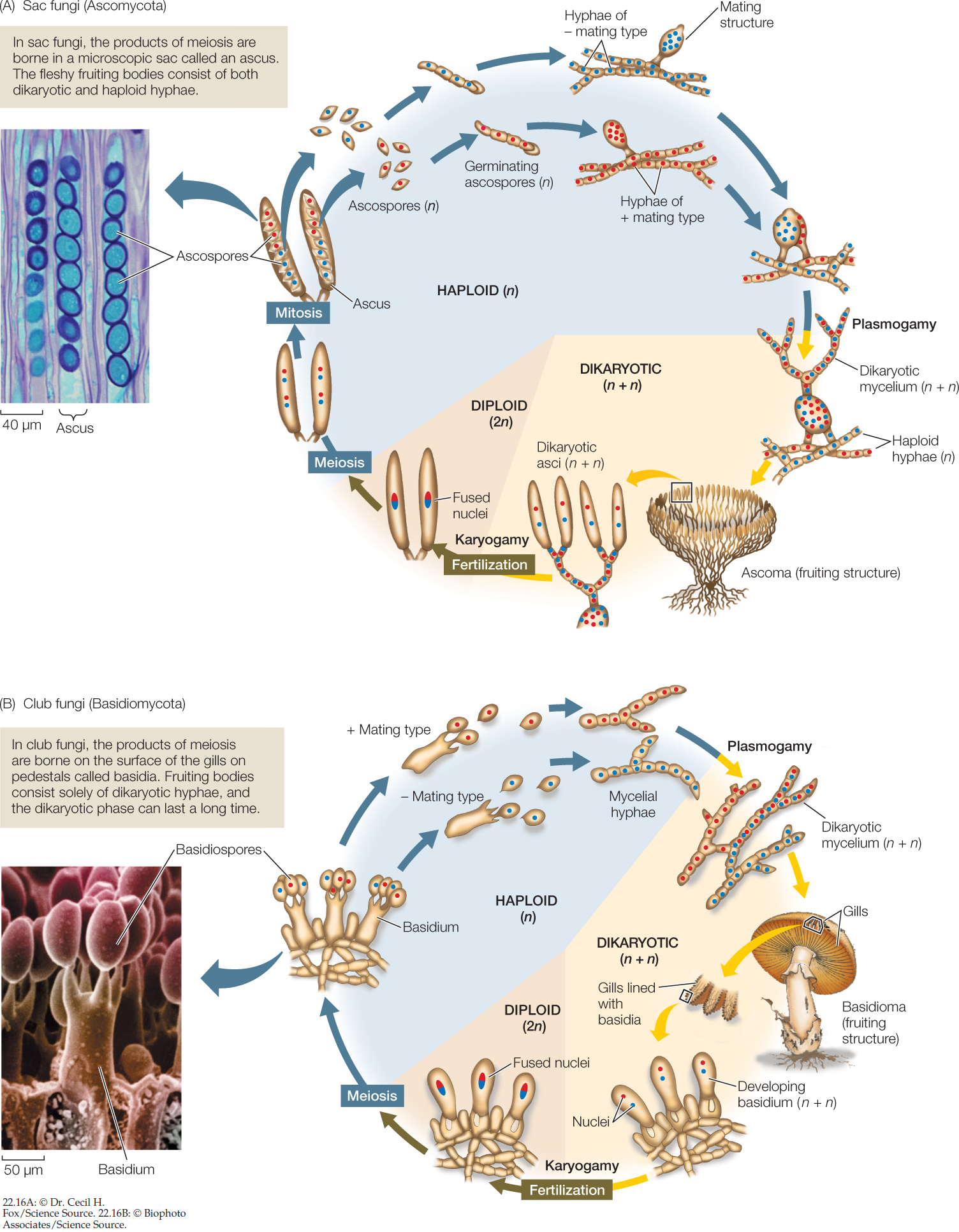



Hillis2e Ch22




Biology 2e Biological Diversity Fungi Classifications Of Fungi Oer Repository Affordable Learning Louisiana



What Is The Difference Between Ascomycota And Basidiomycota Pediaa Com



Fungus Wikipedia



5 What Stage Structure Of Zygomycoya Is Diploid Chegg Com




Lab Practical 1 Survey Of The Kingdom Fungi Flashcards Quizlet




Club Moss Stem Microscopic Photography Plant Structure Nature Beauty
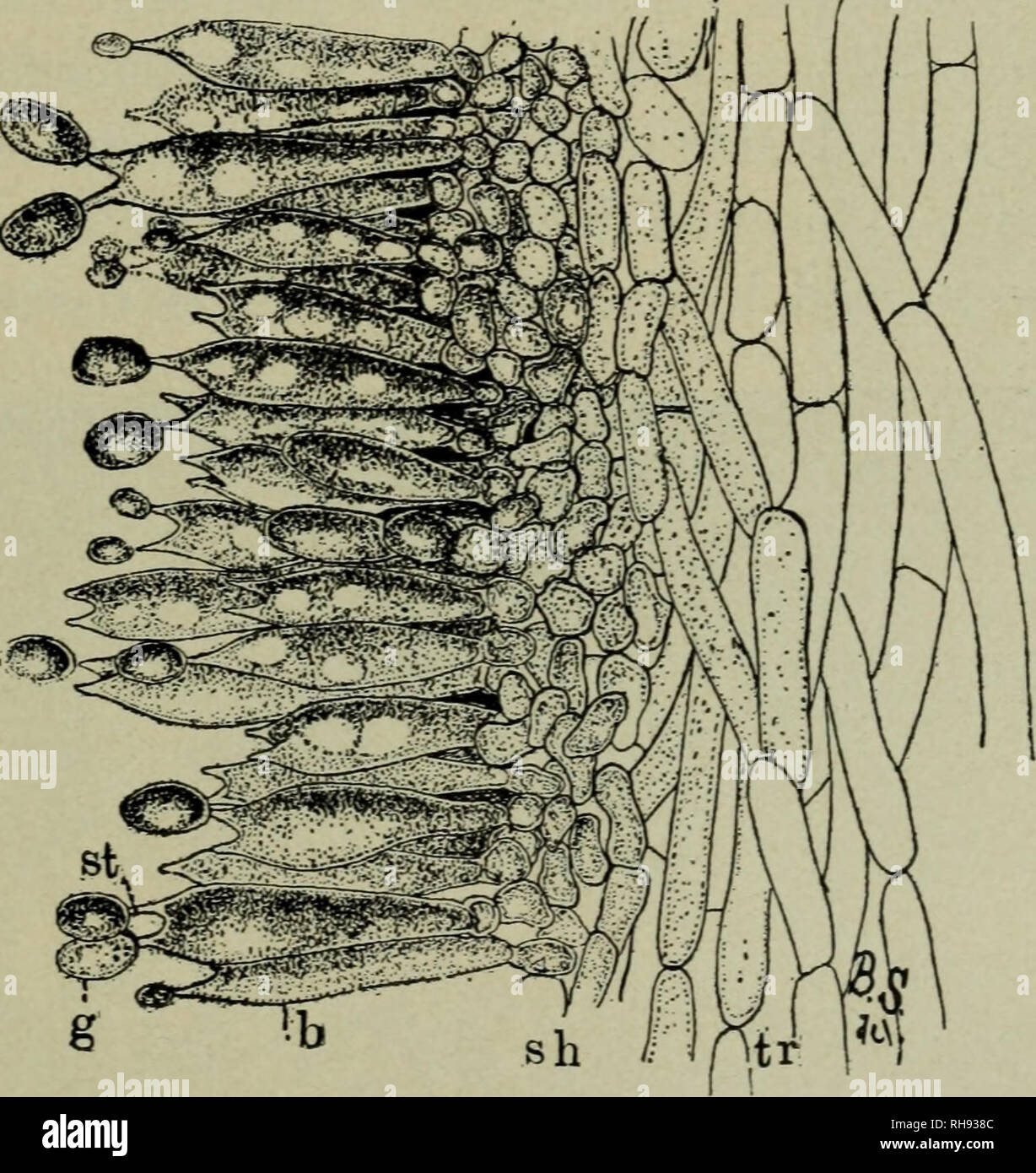



Botany For High Schools Botany Fig 268 The Cultivated Mushroom Agaricus Campestris Cap Is Attached Directly To The Substratum These Thin Plates Or Lamellcej Are Covered With The Club Shaped Structures Or




The Kingdom Fungi These Morels Are A Type Of Fungus Prized By Many People For Their Distinctive Flavor Unlike The Violets Fungi Are Not Plants And Do Ppt Download



Basidiomycota




The Secret World Of Fungi The Wildlife Trust For Lancashire Manchester And North Merseyside




5 Fungi




Fungi Microbiology




Kitan Club Mushroom Led Blind Box Toy Cactus Jungle
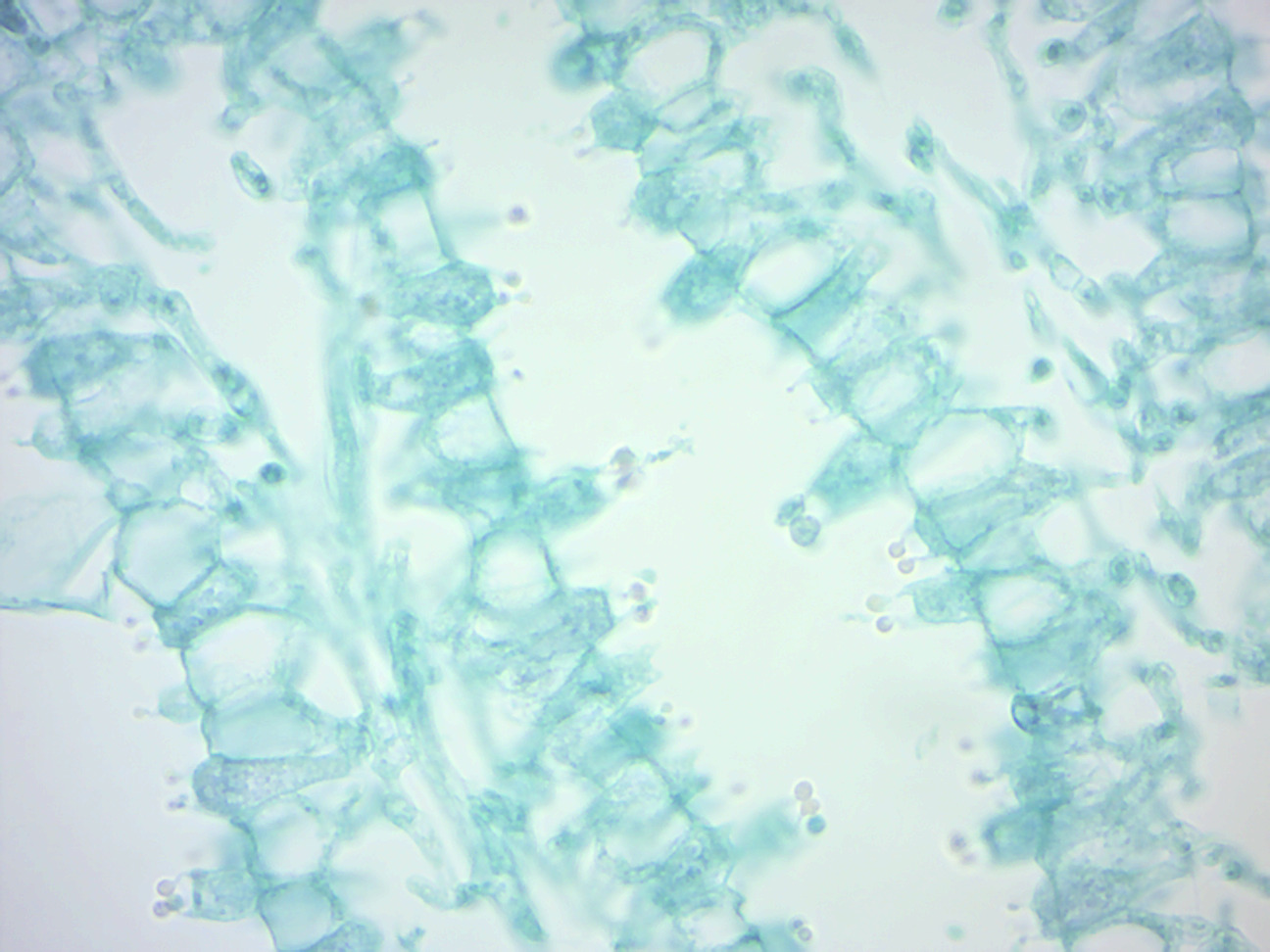



4 Fungi Laboratory Manual For Sci104 Biology Ii At Roxbury Community College
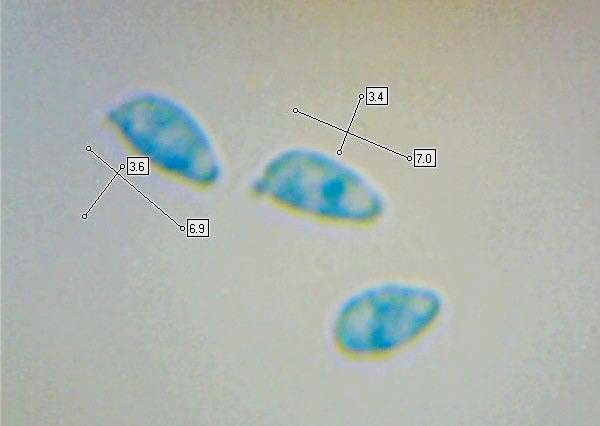



Clavulinopsis Laeticolor Handsome Clubfungus




Pdf Clavariadelphus Pakistanicus Sp Nov A New Club Fungus Basidiomycota Gomphales From Himalayan Moist Temperate Forests Of Pakistan
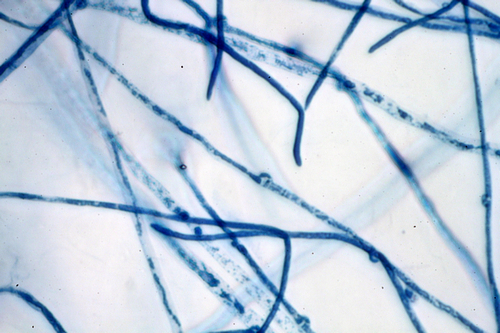



Club Fungi




Club Shaped Conidia Of Fungal Isolates From Marama Pods Download Scientific Diagram




Fungi Protist Prezi By Nini Ho




Fungi Microbiology




16 3 Macrofungi Biology Libretexts



Nick Baker S Hidden Britain Pressreader



Basidiomycota
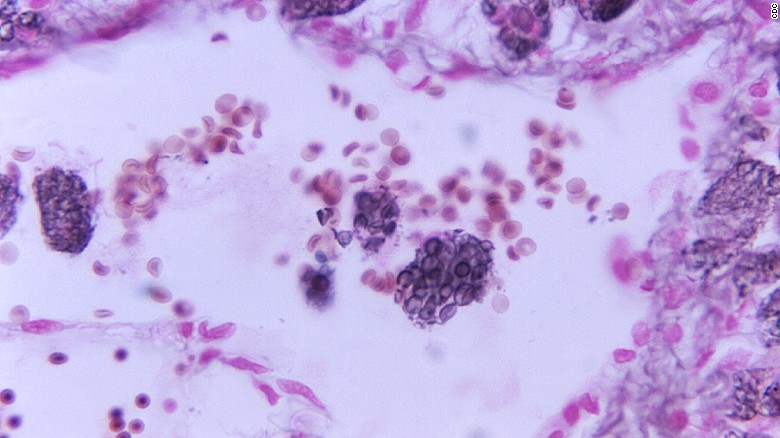



Fungal Diseases Under The Microscope
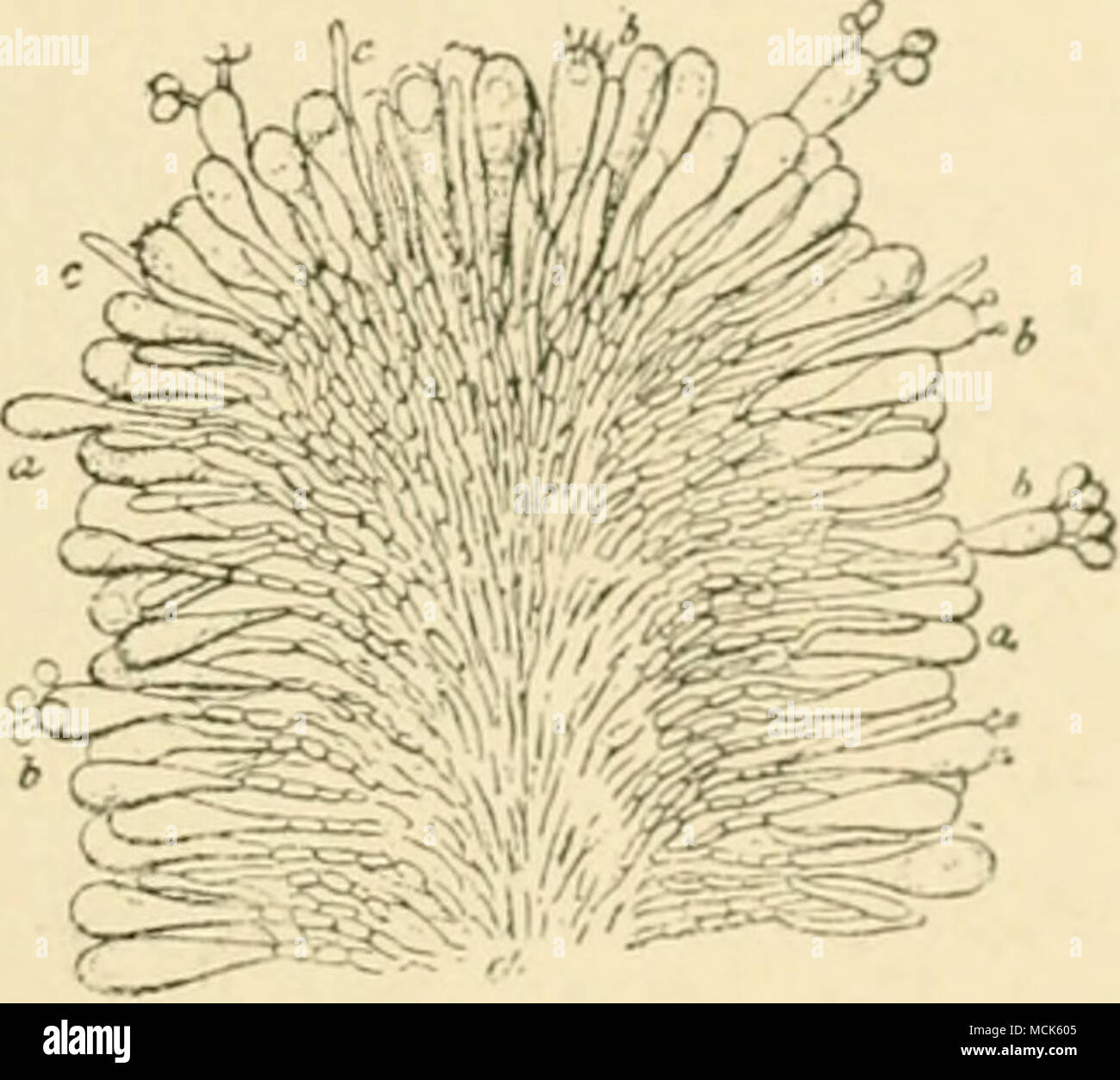



Hymenial Layer High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Classification And Importance Of Fungi




Ppt Club Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
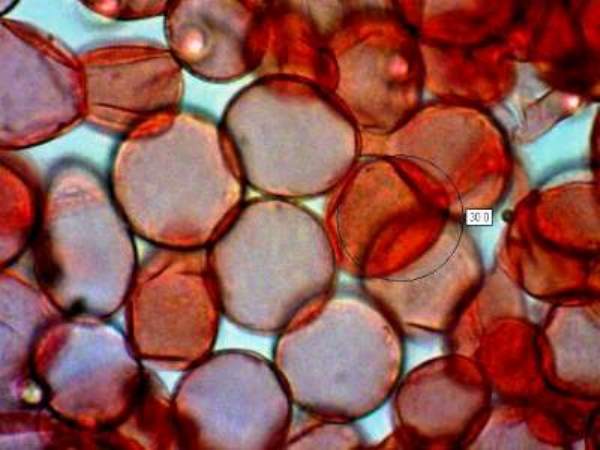



Microscopy Of Spores Hyphae Cystidia Trama To Identify Fungi



Experiment 24 General Medical Microbiology Lab




Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual



Bo9s Uvfpoxgsm



Basidiomycota
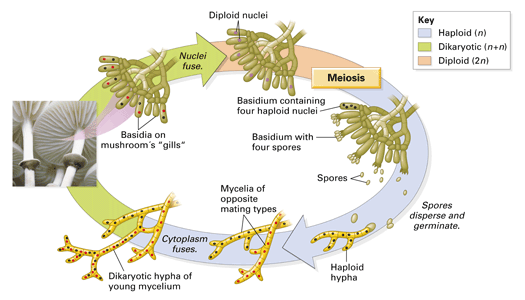



Chapter 18 Concept 18 2




21 2 Classification Of Fungi Ppt Video Online Download
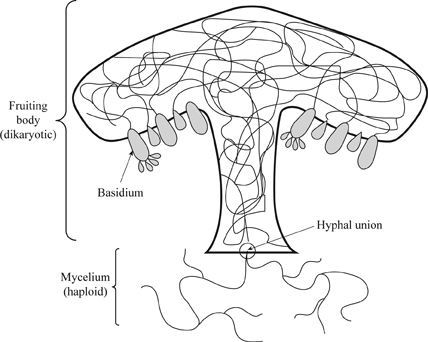



Definition Of The Major Groups Of Fungi Chegg Com




Kingdom Fungi Continued Fungal Phyla 3 Phyla But
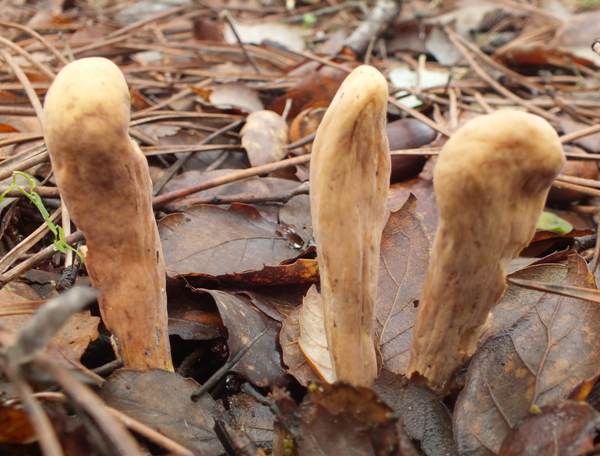




Clavariadelphus Pistillaris Giant Club Fungus Identification



1




Fungi Definition Types And Examples Biology Dictionary



Q Tbn And9gctane6 Nsvtfdytney4jyocsxdwjospdiypiltnapuhte33x5zp Usqp Cau




Fungi Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Ctvalley Bio
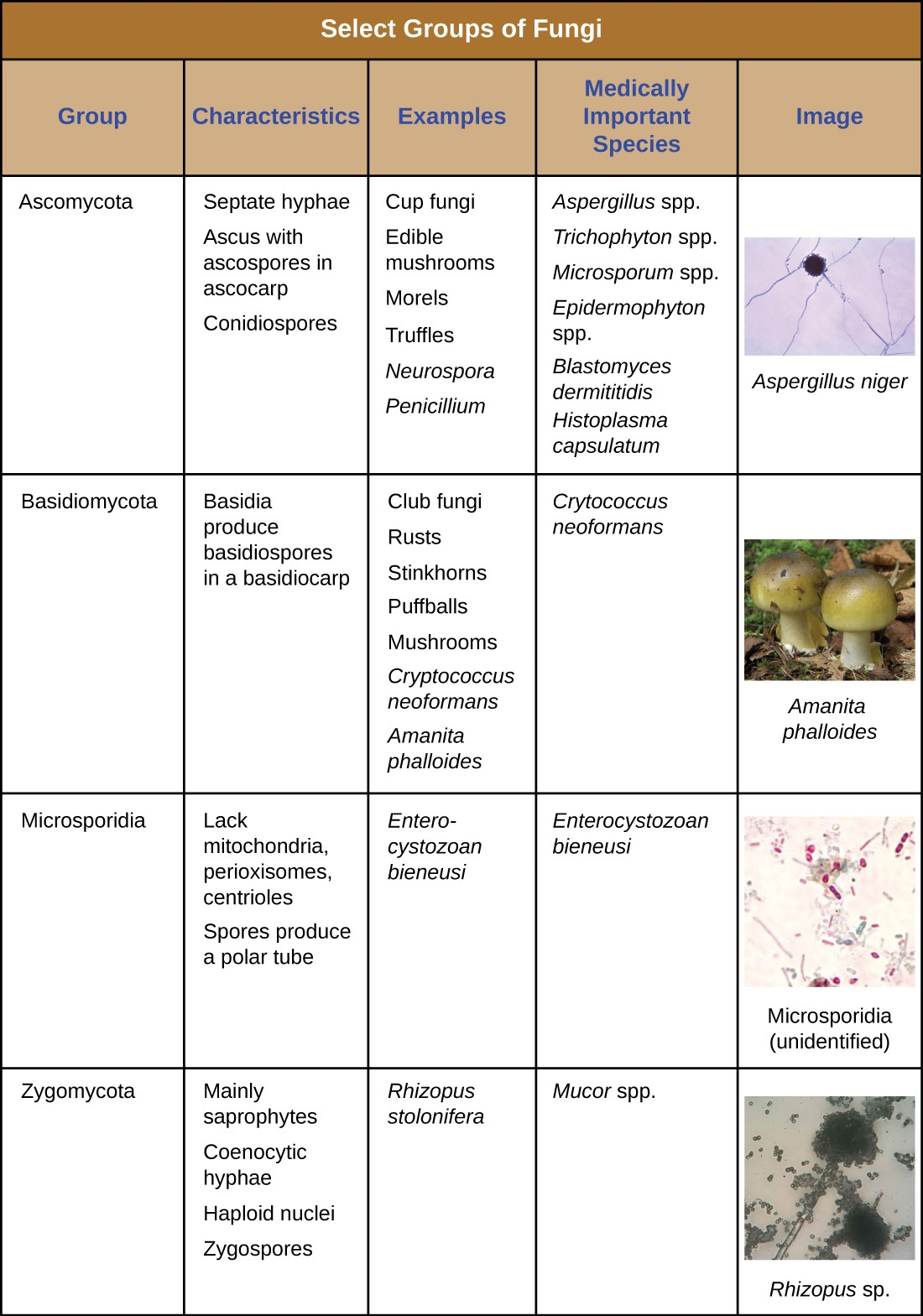



4 3 Fungi Allied Health Microbiology




Fungi 1




Club Fungi Large Images




Club Fungi Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




47 Identifying Fungi Biology Libretexts



Kingdom Fungi Definition Ppt Video Online Download
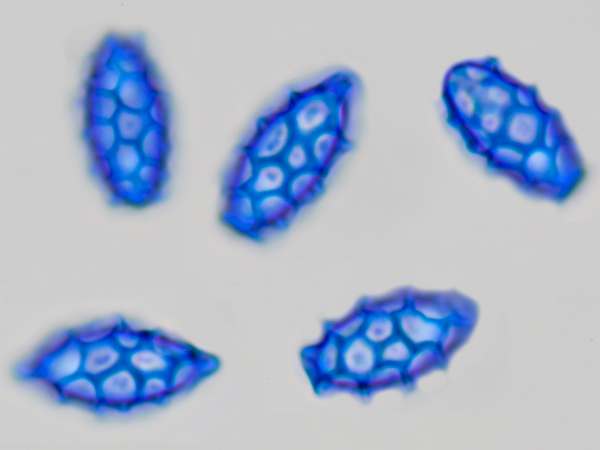



Microscopy Of Spores Hyphae Cystidia Trama To Identify Fungi



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes




Club Fungi Fungi Painting Club



Bil 160 Lecture 17




2 458 Basidiomycota Photos Free Royalty Free Stock Photos From Dreamstime


